Table Of Content
- 1
- 2 Part 1: Understanding and Addressing Rabbit Aggression
- 3 Part 2: Strategies for Managing and Preventing Rabbit Aggression
- 3.0.1 1. Advanced Training Techniques
- 3.0.2 2. Behavior Modification
- 3.0.3 3. Safe Handling Practices
- 3.0.4 4. Providing Escape Routes
- 3.0.5 5. Balanced Diet
- 3.0.6 6.Environmental Enrichment
- 3.0.7 7. Bonding and Socialization
- 3.0.8 8. Neutering and Spaying
- 3.0.9 9. Consistency and Routine
- 3.0.10 10. Patience and Persistence
- 3.0.11 11. Medical Evaluation
- 3.0.12 12. Seeking Professional Help
- 4 Conclusion: Fostering a Harmonious Bond
Part 1: Understanding and Addressing Rabbit Aggression
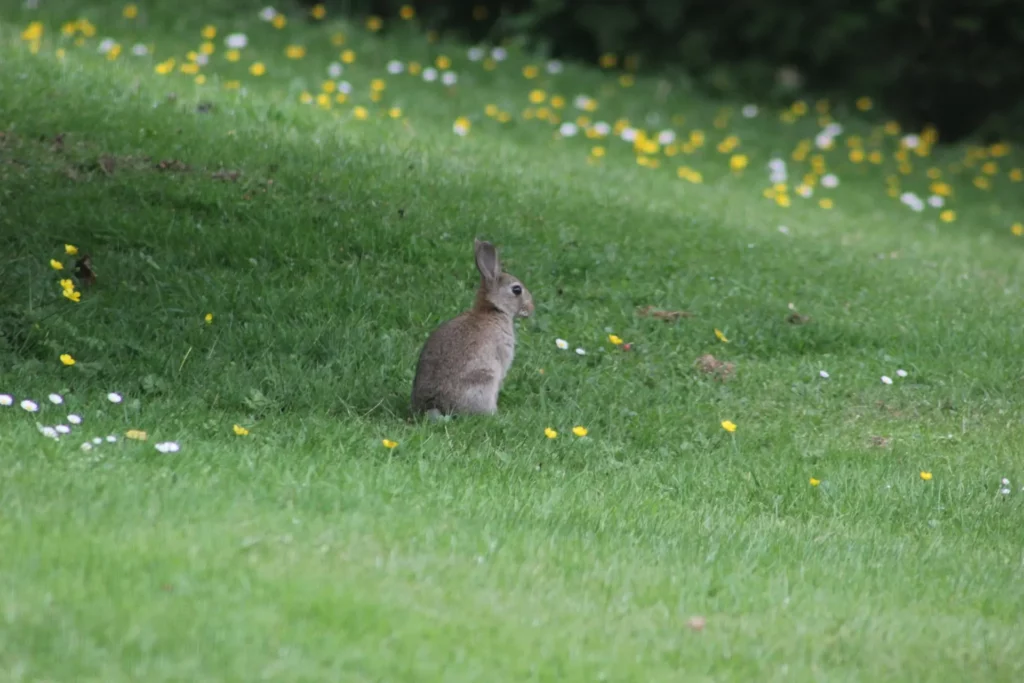
Rabbits are adored as gentle and affectionate pets, yet like any creatures, they may display aggressive behavior. It’s vital for rabbit owners to learn how to handle rabbit aggression effectively. Aggressive behavior in rabbits can arise due to factors like fear, territorial instincts, hormonal changes, and illness. In this first part, we’ll delve into the causes of rabbit aggression and explore ways to manage and prevent it.
1. The Nature of Rabbit Aggression
Understanding rabbit aggression is crucial. Rabbits, as prey animals, use aggression as a defense mechanism. Identifying triggers for aggression is the initial step in handling rabbit aggression and creating a peaceful rabbit-human relationship.
2. Fear and Stress
Rabbits can become aggressive when stressed or threatened. Common stressors include loud noises and sudden movements. A calm environment minimizes aggressive outbursts and contributes to better rabbit behavior, enhancing the human-rabbit bond.
3. Territorial Behavior
Territorial aggression can stem from rabbits feeling their space invaded. Unspayed or unneutered rabbits might show this behavior due to hormones. Spaying/neutering helps manage territorial rabbit aggression and promote a harmonious home environment.
4. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in unaltered rabbits, can lead to aggression, especially in males. Neutering can alleviate hormonal rabbit aggression, resulting in more balanced and manageable rabbit behavior patterns.
5. Illness and Pain
Aggression might signal underlying health problems or pain. Regular vet check-ups can rule out medical causes of rabbit aggression and ensure overall rabbit well-being, contributing to positive rabbit-human interactions.
6. Social Hierarchy
Rabbits display aggression when establishing dominance. Introducing rabbits gradually and allowing them to establish their pecking order minimizes aggressive confrontations and fosters a peaceful multi-rabbit household dynamic.
7. Handling Aggression
When confronted with rabbit aggression, maintaining composure is paramount. Abstaining from reciprocating with aggression and instead adopting a composed demeanor is instrumental in deescalating the situation. With a gradual retreat, rabbits are afforded the opportunity to regain their composure and minimize the intensity of their aggressive behavior.
8. Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement curbs rabbit aggression. Reward desired behavior with treats, associating human interaction positively and encouraging improved rabbit behavior, strengthening the human-rabbit connection.
9. Enrichment and Playtime
Boredom can lead to aggression. Enriching activities and playtime reduce pent-up energy and prevent rabbit aggression, promoting a happy and well-adjusted rabbit, and a harmonious human-rabbit relationship.
For more insights into rabbit bonding and managing aggression, you can visit these helpful articles on Rabbit Care Mastery:
- Bonding Bunnies: Introducing Rabbits to Each Other
- Creating Harmony: The Magic of Bonding Two Female Rabbits
- Bonding Two Dominant Rabbits
Part 2: Strategies for Managing and Preventing Rabbit Aggression
Having delved into the causes of rabbit aggression in the preceding segment, we will now delve deeper into strategic methodologies tailored to managing and forestalling such behavior. These approaches are indispensable in engendering a balanced and harmonious rapport between rabbits and their human companions.
1. Advanced Training Techniques
In conjunction with positive reinforcement, the deployment of advanced training techniques is a judicious endeavor in the context of addressing rabbit aggression. Desensitization, a gradual exposure to aggression triggers, facilitates the gradual attenuation of perceived threats, thereby paving the way for the amelioration of aggressive tendencies.
2. Behavior Modification
Consultation with accomplished animal behaviorists is a pragmatic recourse for the modification of rabbit aggression. These experts are adept at scrutinizing aggression triggers and contriving an incisive blueprint for rechanneling such behaviors in a constructive direction.
3. Safe Handling Practices
When contending with aggressive rabbits, adherence to safe handling protocols is of paramount significance. Employing a towel or blanket as a gentle restraint during interactions is conducive to averting bites or scratches. Gradually familiarizing rabbits with handling bolsters trust and concurrently, reduces proclivities for aggression.
4. Providing Escape Routes
Cultivating a rabbit-friendly habitat replete with concealing nooks can assuage feelings of fear and distress. The provision of escape routes confers rabbits the option of retreating to a safe enclave, consequently curtailing the propensity for aggressive reactions.
5. Balanced Diet
The nutritional facet wields considerable influence over behavior. Administering a well-rounded diet encompassing hay, fresh vegetables, and quality pellets can curtail mood fluctuations and subsequently, mitigate rabbit aggression.
6.Environmental Enrichment
The introduction of diversifying elements such as toys, tunnels, and puzzle feeders can assuage aggression stemming from monotony. The periodic rotation and infusion of novel enrichment items further counteract the exacerbation of aggressive tendencies.
7. Bonding and Socialization
For households harboring multiple rabbits, fostering bonds and facilitating socialization is pivotal in forestalling aggressive behavior within the collective. Prudent introductions in neutral settings and supervised interactions lay the groundwork for a harmonious hierarchy.
8. Neutering and Spaying
Addressing the hormonal underpinnings of aggression is indispensable. The decision to spay or neuter rabbits serves to curtail hormonal influences, thereby engendering a more placid temperament and mitigating instances of rabbit aggression.
9. Consistency and Routine
Rabbits are creatures of habit. A consistent regimen encompassing feeding, play, and interaction imparts a sense of predictability, assuaging anxiety and concurrently mitigating proclivities for aggression.
10. Patience and Persistence
The nuanced process of modifying rabbit aggression necessitates time and unwavering patience. The pursuit of behavior modification and the establishment of a nurturing environment requires sustained efforts, culminating in the gradual dissipation of aggressive manifestations.
11. Medical Evaluation
Should instances of aggression persist, a comprehensive medical assessment is warranted. Underlying health issues could potentially underpin such behavior, necessitating veterinary intervention to effectuate requisite remedies.
12. Seeking Professional Help
In cases of severe aggression, enlisting the expertise of a veterinarian or proficient behaviorist is prudent. The insights and tailored strategies offered by these professionals prove instrumental in navigating the complexities of rabbit behavior and ultimately, reinstating harmony.
Conclusion: Fostering a Harmonious Bond
The management and prevention of rabbit aggression is central to nurturing a gratifying human-rabbit relationship. The strategic identification of aggression causes, coupled with the judicious implementation of efficacious approaches, engenders an environment conducive to positive rabbit behavior and, by extension, a harmonious connection. In the tapestry of human-rabbit companionship, the pursuit of tranquility is a laudable endeavor, underscoring the immeasurable rewards that ensue from a serene and affectionate rapport.